
unplugin-vue-cssvars
🌀 A vue plugin that allows you to use vue3's CSSVars feature in css files
English | 中文
Feature
- 🧩 It is a function extension of vue
- 🌈 Compatible with multiple bundled platforms(vite、webpack)
- ⛰ Support css, sass, scss, less, stylus
- ⚡ Support hmr
Core Strategy
1.When using the development server, unplugin-vue-cssvars will analyze the referenced css file from the component, and inject styles in the transformation code of @vitejs/plugin-vue 2.When building, unplugin-vue-cssvars will analyze the referenced css file from the component and inject it into sfc, don't worry about generating redundant code, packaging tools (such as vite) will automatically handle it.
Install
bash
npm i unplugin-vue-cssvars -DOr
bash
yarn add unplugin-vue-cssvars -DOr
bash
pnpm add unplugin-vue-cssvars -DUsage
- use plugin and set options
Vite
ts
// vite.config.ts
import { defineConfig } from 'vite'
import { viteVueCSSVars } from 'unplugin-vue-cssvars'
import vue from '@vitejs/plugin-vue'
import type { PluginOption } from 'vite'
export default defineConfig({
plugins: [
vue(),
viteVueCSSVars({
include: [/.vue/],
includeCompile: ['**/**.scss'],
server: false,
}) as PluginOption,
],
})Rollup
ts
// rollup.config.js
import { rollupVueCSSVars } from 'unplugin-vue-cssvars'
export default {
plugins: [
rollupVueCSSVars(/* options */),
],
}Webpack
ts
// webpack.config.js
module.exports = {
/* ... */
plugins: [
require('unplugin-vue-cssvars').webpackVueCSSVars({ /* options */ }),
],
}Vue CLI
ts
// vue.config.js
module.exports = {
configureWebpack: {
plugins: [
require('unplugin-vue-cssvars').webpackVueCSSVars({ /* options */ }),
],
},
}ESBuild
ts
// esbuild.config.js
import { build } from 'esbuild'
import { esbuildVueCSSVars } from 'unplugin-vue-cssvars'
build({
plugins: [esbuildVueCSSVars(/* options */)],
})- use
v-bind-m
// foo.css
.foo{
color: v-bind-m(fontColor)
}- use alias
For example you have the following project structure:
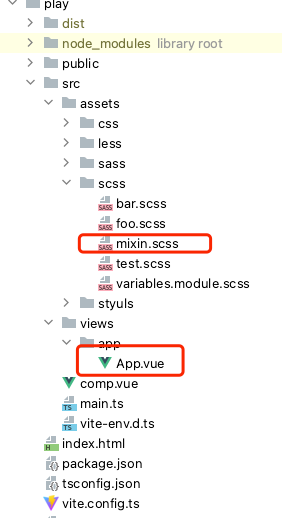
// App.vue
<template>
<div class="scss">
app
</div>
</template>
<style lang="scss" scoped>
@import '@/assets/scss/mixin';
</style>Then you can configure like this
// vite.config.ts
import { resolve } from 'path'
import { defineConfig } from 'vite'
import vue from '@vitejs/plugin-vue'
import { viteVueCSSVars } from '../dist'
export default defineConfig({
resolve: {
alias: {
'@': resolve(__dirname, './src'),
},
},
plugins: [
vue(),
viteVueCSSVars({
include: [/.vue/],
includeCompile: ['**/**.scss'],
alias: {
'@': resolve(__dirname, './src'),
},
}),
],
})Option
typescript
export interface Options {
/**
* Provide path which will be transformed
* @default process.cwd()
*/
rootDir?: string
/**
* RegExp or glob to match files to be transformed
*/
include?: FilterPattern
/**
* RegExp or glob to match files to NOT be transformed
*/
exclude?: FilterPattern
/**
* Specify the file to be compiled, for example,
* if you want to compile scss, then you can pass in ['** /**.sass']
* @property { ['** /**.css', '** /**.less', '** /**.scss', '** /**.sass', '** /**.styl'] }
* @default ['** /**.css']
*/
includeCompile?: Array<string>
/**
* Flag whether to start with server at development time,
* because unplugin-vue-cssvars uses different strategies for building and server development
* If it is not passed in vite, unplugin-vue-cssvars will automatically
* recognize the command of config to determine the server value
* @default true
*/
server?: boolean
/**
* alias
* @default undefined
*/
alias?: Record<string, string>
}Tips
● Rules When Transforming Analysis
- In
sfc, if@importspecifies a suffix, the conversion analysis will be performed according to the suffix file, otherwise the conversion analysis will be performed according to thelangattribute of the currentstyletag (defaultcss) - Rules in
css:cssfiles can only referencecssfiles, and only files withcsssuffixes will be parsed. - Rules in
scss,less,stylus:scss,less,stylusfiles can refer tocssfiles, and correspondingscssorlessfiles orstylusfiles, Prioritize conversion analysis of files with preprocessor suffixes, if the file does not exist, analyze itscssfile
● Variable extraction rules in SFC
- For
script setup,unplugin-vue-cssvarswill extract all variables to match.
<script setup>
const color = 'red'
</script>- For
composition api,unplugin-vue-cssvarswill extractsetupfunction return variables for matching.
<script>
import { defineComponent } from 'vue'
export default defineComponent( {
setup(){
const color = 'red'
return {
color
}
}
})
</script>- For
options api,unplugin-vue-cssvarswill extractdatafunction return variables for matching.
<script>
export default {
data(){
const color = 'red'
return {
color
}
}
}
</script>- For normal
script,unplugin-vue-cssvarswill extract all variables to match.
<script>
const color = 'red'
</script>● Variable conflict rules in SFC
- In sfc, there are options API and composition API, and all variables will be merged. If there are conflicts in variables, the syntax that appears later will take precedence (for example, if options API is written first and composition API is written later, composition API takes precedence).
- There are
script setup,options apiandcomposition apiinsfc, all variables will be merged, if there is a variable conflict,script setupwill take precedence - Ordinary
scriptinsfcwill not exist at the same time asoptions apiandcomposition api - If the normal
scriptexists insfc, there must bescript setup - Common
scriptandscript setupvariables insfcwill be merged, if there is a variable conflict,script setupwill take precedence
● Priority after style injection
- Starting from
sfc, analyze thecssfiles referenced in thestyletag, and in accordance with the order of references in thecssfiles, they will be promoted in depth-first order and injected intosfc. - After being injected into
sfc, its priority is completely determined by the compiler of@vue/compiler-dom.